How to Use Fan-Forced and Conventional Oven Settings Correctly
Fan-forced (convection) and conventional oven settings can impact cooking times, texture, and browning. This post will dive into each setting’s strengths and when to use them, making it easier to choose the best option for each recipe.
Understanding Oven Types
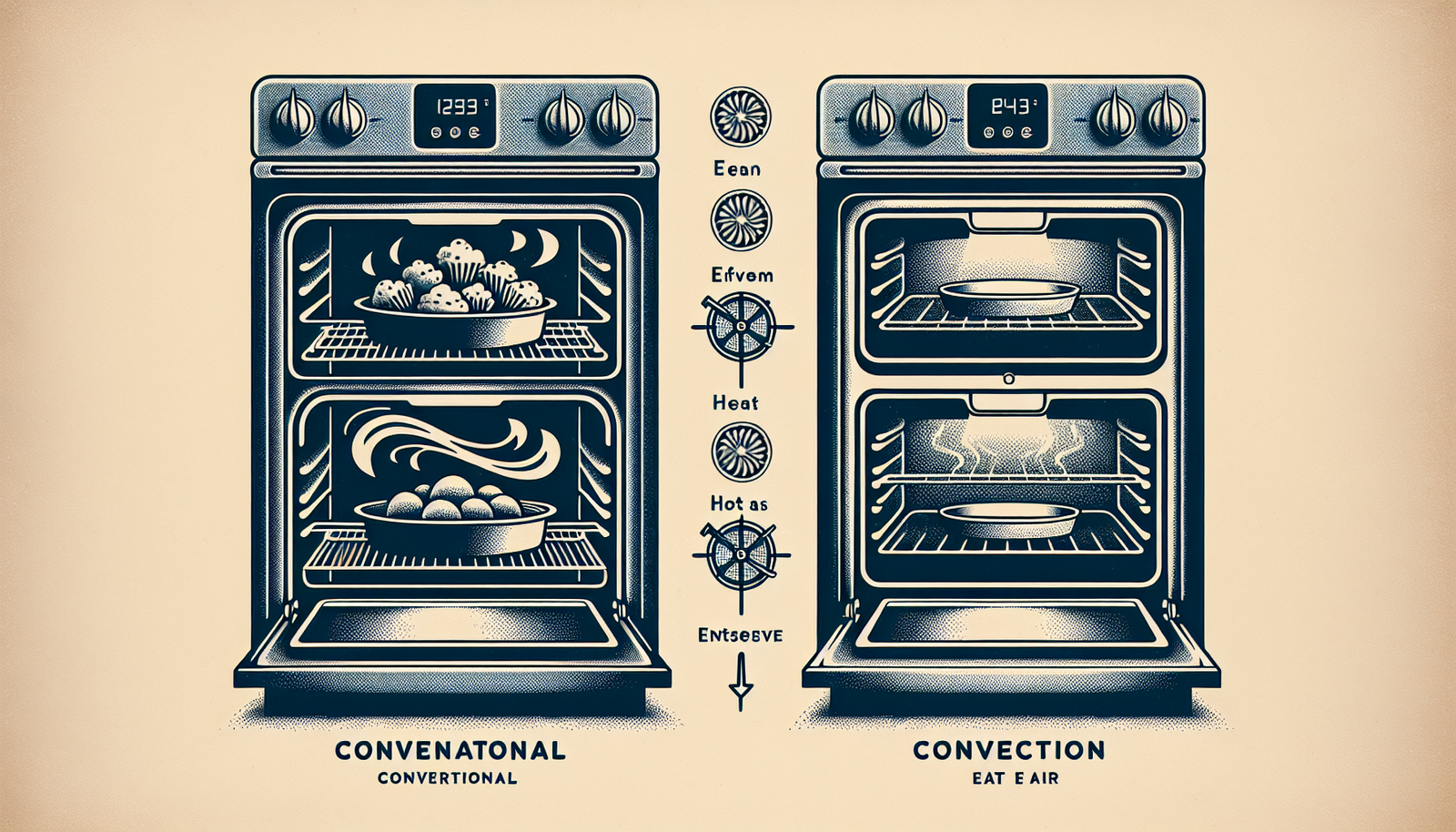
Ovens are central to any kitchen, and understanding the types available can transform your cooking experience. Two common types, fan-forced and conventional ovens, each serve unique purposes and offer distinct features. Knowing these differences helps ensure your meals are cooked to perfection. This section explores what sets them apart, how they distribute heat, and their typical culinary uses.
Differences between Fan-Forced and Conventional
Fan-forced ovens, also known as convection ovens, incorporate a fan and exhaust system. This setup circulates hot air around the food, resulting in faster cooking times and even heat distribution. In contrast, conventional ovens rely on radiant heat from top and bottom elements without air circulation. This can lead to uneven cooking, particularly if the oven is crowded.
Understanding these differences helps you choose the right oven for your cooking needs. Fan-forced ovens excel in efficiency and uniformity, making them perfect for busy cooks. Conventional ovens offer a more traditional approach, appreciated by those who enjoy slow, deliberate cooking processes.
Heat Distribution Comparison
Heat distribution plays a critical role in cooking quality. Fan-forced ovens boast superior heat distribution due to their internal fan system. The fan ensures even heat reaches all parts of the food, reducing the risk of cold spots and overcooked edges.
Conventional ovens, however, can have hot and cold zones due to their reliance on static heat. This uneven distribution requires strategic placement of dishes and potentially rotating them during cooking. Recognizing these differences allows you to optimize your oven’s capabilities, ensuring consistently well-cooked meals.
Common Uses for Each Type
Fan-forced ovens are versatile, suitable for baking, roasting, and even dehydrating foods. Their efficiency makes them ideal for high-volume cooking and recipes requiring precise temperature control. Roasting vegetables or meats benefits from the even heat, ensuring a crispy outside and tender inside.
Conventional ovens, on the other hand, shine in baking tasks requiring gentler heat. They’re perfect for dishes like soufflés, custards, and pies, where a slow build-up of heat prevents cracking or drying out. Both oven types serve vital roles, and understanding when to use each can elevate your cooking styles.
Benefits of Fan-Forced Ovens
Fan-forced ovens bring a host of advantages to modern kitchens. Their design and functionality cater to both professional chefs and home cooks seeking convenience and efficiency. This section delves into the primary benefits, highlighting why fan-forced ovens are a popular choice for many.
Reduced Cooking Times
One of the standout benefits of fan-forced ovens is their ability to significantly reduce cooking times. The consistent circulation of hot air cooks food faster than conventional ovens. This accelerated process is not only time-saving but can also enhance the flavor and texture of dishes.
Fan-forced ovens are particularly useful in busy kitchens where time is of the essence. Whether you’re preparing a weeknight meal or a large holiday feast, the speed and efficiency of a fan-forced oven can make all the difference.
Even Heat for Baking
Baking requires precise temperature control, and fan-forced ovens excel in this area. The even distribution of heat ensures that baked goods cook uniformly, resulting in perfect cakes, cookies, and bread every time.
Fan-forced ovens eliminate the need to rotate trays, allowing for a more hands-off baking experience. This consistency is crucial for delicate pastries and breads where even minor temperature fluctuations can affect the final product.
Ideal for Roasting Meats
Roasting meats to perfection involves achieving the right combination of a crispy exterior and a juicy interior. Fan-forced ovens are ideal for this task, providing even heat that helps render fats and promote browning.
The efficient cooking process locks in juices, enhancing the flavor and tenderness of the meat. Whether you’re preparing a simple weeknight dinner or a special holiday roast, a fan-forced oven can deliver consistently impressive results.
When to Use Conventional Settings
While fan-forced ovens offer numerous advantages, conventional settings hold their own special place in the culinary world. They cater to specific dishes that benefit from traditional cooking methods. This section explores when and why you should choose conventional oven settings for your culinary endeavors.
Better for Delicate Baked Goods
Delicate baked goods, such as soufflés, macarons, and meringues, thrive in conventional ovens. The gentle, static heat helps these sensitive items rise slowly and evenly. This controlled environment reduces the risk of cracking or collapsing.
Conventional settings provide the consistent, gentle heat needed for these intricate creations. For bakers who prioritize precision and detail, conventional ovens are a trusted ally in the kitchen.
Avoids Over-Crisping
Certain dishes, like casseroles, custards, and some baked goods, benefit from a less aggressive cooking environment. Conventional ovens allow for a slower, more controlled cook, preventing over-crisping or drying out.
The lack of circulating air in conventional ovens maintains moisture, preserving the intended texture of your dishes. Understanding when to opt for this setting can be the difference between a dry dish and a perfectly balanced one.
How to Adjust Recipes for Conventional Baking
Adapting recipes for conventional baking involves minor adjustments that can make a significant impact. Start by increasing the cooking time and lowering the temperature slightly compared to fan-forced settings.
Monitoring the dish closely will help avoid overcooking. For certain recipes, covering them with foil can help maintain moisture. With these adjustments, you can confidently use conventional settings without compromising on quality.
Conclusion
Choosing between fan-forced (convection) and conventional oven settings is essential for achieving the best results for different dishes. Fan-forced ovens provide even heat distribution, which shortens cooking time and enhances browning—perfect for roasting meats or baking multiple trays at once. Conventional ovens, however, are often preferable for delicate baked goods, as they maintain a more static environment that can prevent items from drying out or over-browning. Understanding the strengths of each setting will give you more flexibility in the kitchen, allowing you to cook or bake a wide range of dishes with optimal results.
FAQ
What is a fan-forced oven setting?
A fan-forced oven uses a fan to circulate hot air, ensuring even heat distribution. This feature enables efficient cooking by maintaining consistent temperatures throughout the oven.
When should I use conventional settings?
Conventional settings, which rely on static heat from top and bottom elements, are ideal for dishes requiring slow and gentle cooking. They’re perfect for casseroles, roasting meats, and baking bread.
Does fan-forced cooking reduce cooking time?
Yes, fan-forced cooking generally reduces cooking time. The circulating hot air speeds up the cooking process, allowing dishes to cook faster and more evenly.
Can I convert recipes between fan-forced and conventional?
Converting recipes is possible. Lower the temperature by about 20°C (35°F) when switching from conventional to fan-forced. Monitor cooking times as they may vary.
Which setting is better for baking?
Fan-forced settings are excellent for uniform baking, especially for cookies and pastries. However, conventional settings excel with delicate bakes like soufflés and some breads.
How do I know if my oven is fan-forced?
Check for a fan symbol or button on the control panel. You may also hear the fan running when the function is active. Consult your oven manual if unsure.











